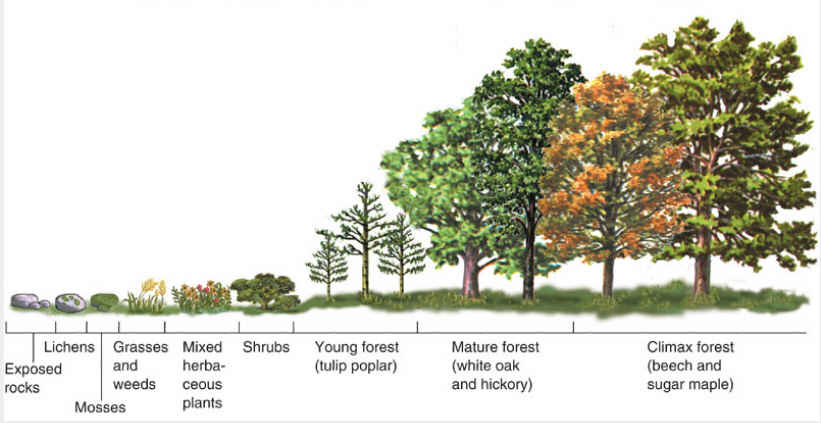
In the absence of disturbance, plant communities undergo a sequence of changes called ecological succession.
- Pioneering species such as
lichens
and mosses build up the soil.
- Herbaceous grasses and forbs follow.
- If there is sufficient precipitation, shrubs and taller woody vegetation move in.
- The succession may proceed to a mature forest and eventually a climax community.
